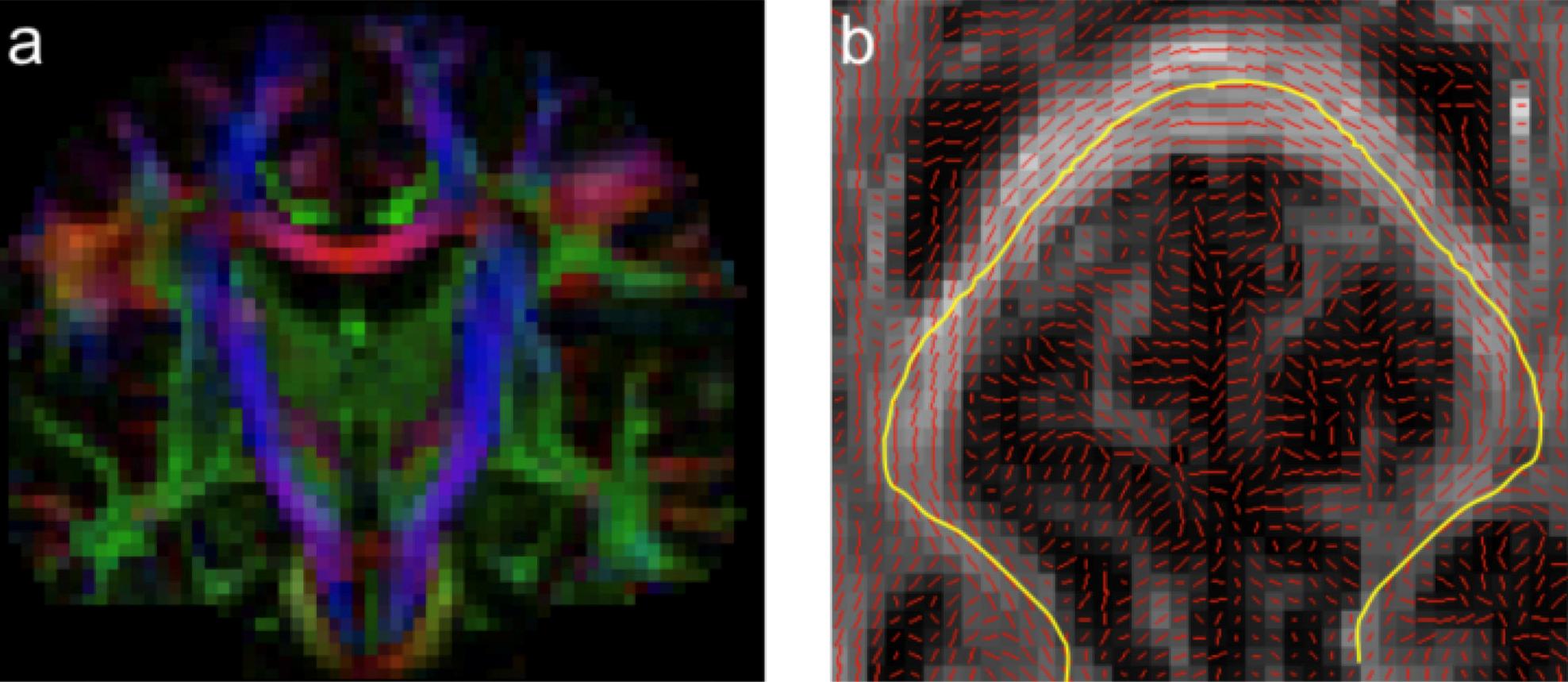
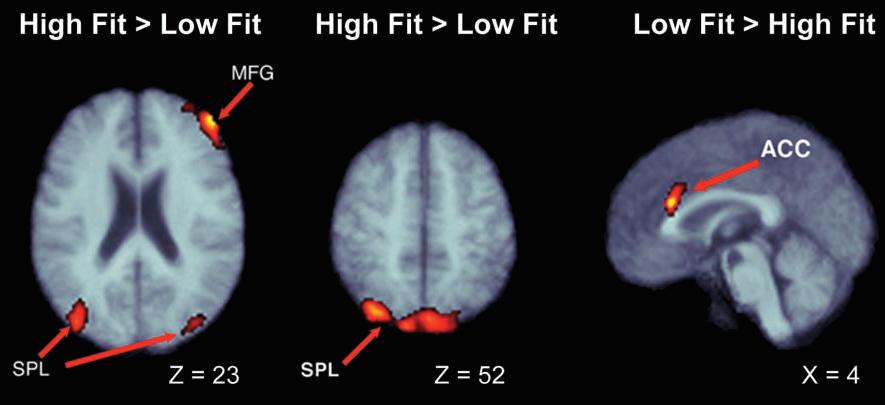
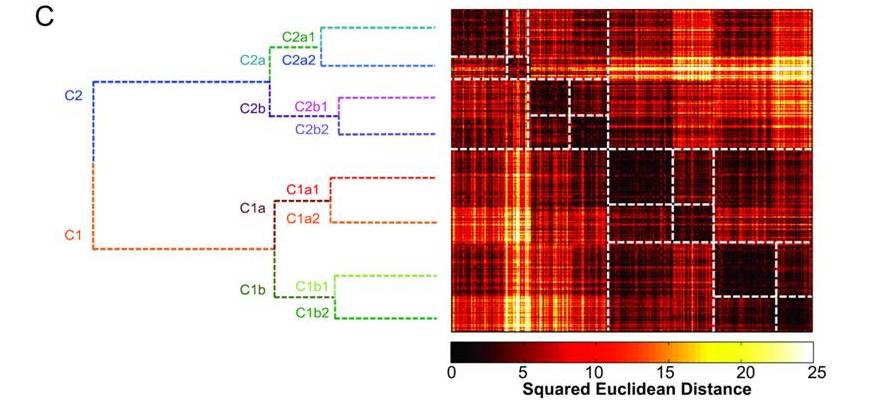
The Center for Biomedical Imaging and Neuromodulation (C-BIN) focuses on the development and application of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques for characterizing brain function and structure in order to improve our understanding, diagnosis and treatment of mental illness.
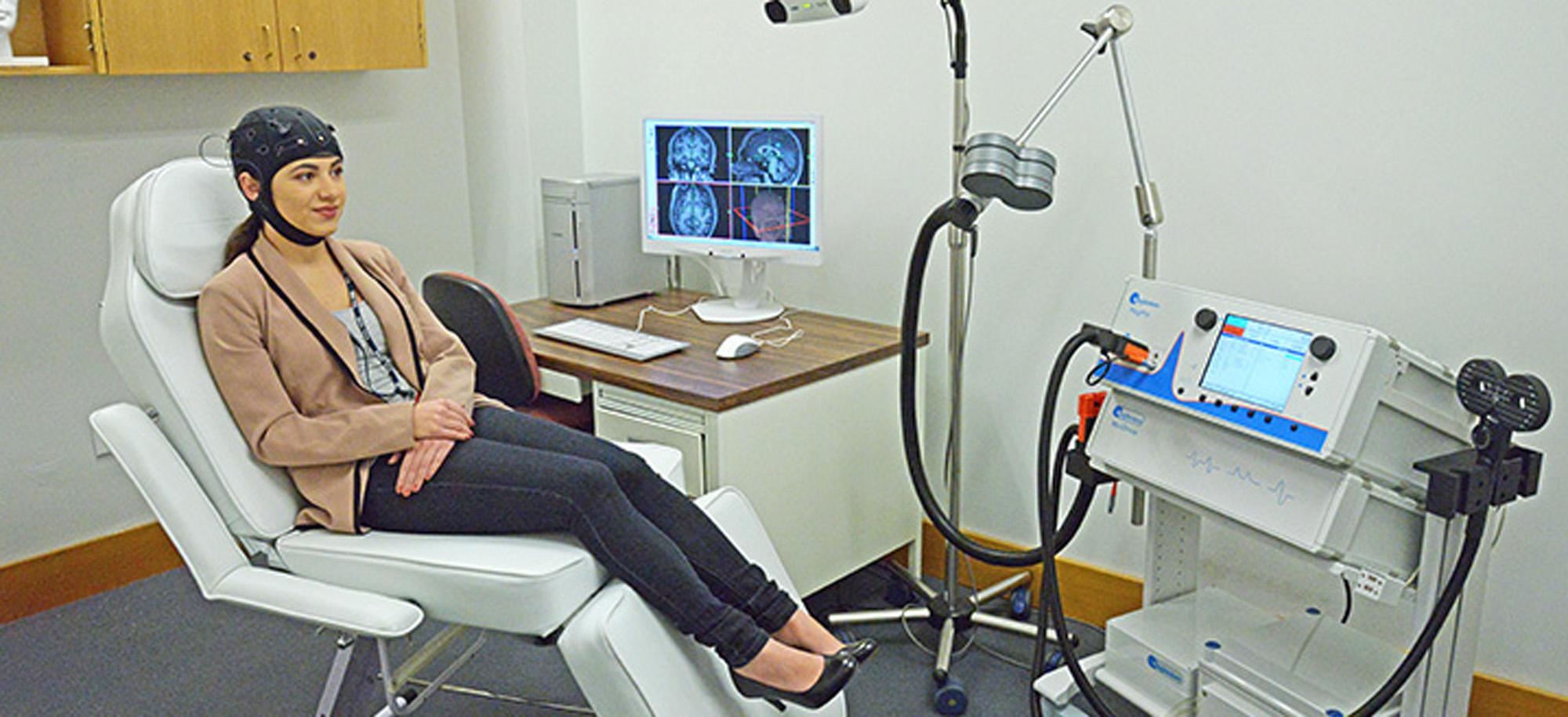
Overview
By mapping brain development and maturation in clinical and non-clinical populations, the Center aims to innovate neurobiological models of mental illness and to develop clinically useful markers to guide diagnosis and treatment. Complementary work focuses on probing brain plasticity and identifying modifiable targets for illness using neuromodulatory techniques (e.g., cognitive training, exercise, non-invasive brain stimulation, and chemogenetics).
Open Science
C-BIN investigators are leaders in promoting the open sharing of neuroimaging data, through initiatives like the 1000 Functional Connectomes Project and its International Neuroimaging Data-Sharing Initiative (INDI). For example, scores of scientists from around the world have downloaded the large-scale, multimodal NKI-Rockland Sample datasets for use in their own research.
A Stimulating Approach
One key area of focus is the evaluation and optimization of the delivery of transcranial brain stimulation approaches, including transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Complementing observational imaging approaches to understanding human brain function are these brain stimulation approaches, which can temporarily alter patterns of neural activity. When applied repeatedly, they have the potential to correct abnormal patterns of brain activity underlying mental illness.